해시(hash)는 정보를 저장하거나 검색할 때 사용하는 자료구조이다. 정보를 어디에 저장할 것인지, 어디서 가져올 것인지 해시 함수를 사용하여 구현한다.
해시 함수는 객체의 특정 정보(키 값)를 매개변수 값으로 넣으면 그 객체가 저장되어야 할 위치나
저장된 해시 테이블 주소(위치)를 반환한다.
따라서 객체 정보를 알면 해당 객체의 위치를 빠르게 검색할 수 있다.
// 자바에서는 인스턴스를 힙 메모리에 생성하여 관리할 때 해시 알고리즘을 사용한다.
hashCode = hash(key); // 객체의 해시 코드 값(메모리 위치 값)이 반환됨
package object;
class Book {
int bookNumber;
String bookTitle;
Book (int booknum, String title) {
this.bookNumber = booknum;
this.bookTitle = title;
}
}
public class ToStringEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book book1 = new Book(200, "개미");
System.out.println(book1);
System.out.println(book1.toString());
System.out.println(book1.hashCode());
}
}
Object 클래스의 toString() 메서드 원형을 다시 보면, getClass().getName() + '@' + Integer.toHexString(hashCode())이다.
우리가 참조 변수를 출력할 때 본 16진수 숫자 값이 '해시 코드 값'이고, 이 값은 자바 가상 머신이 힙 메모리에 저장한
'인스턴스의 주소 값'이다.
자바에서는 두 인스턴스가 같다면 hashCode() 메서드에서 반환하는 해시 코드 값이 같다.
만약, 논리적으로 같은 두 객체도 같은 코드 값을 반환하도록 하려면 hashCode() 메서드를 재정의해야 한다.
또, equals() 메서드를 재정의했다면 hashCode() 메서드도 재정의해야 한다.
package object;
class Book {
int bookNumber;
String bookTitle;
Book (int booknum, String title) {
this.bookNumber = booknum;
this.bookTitle = title;
}
@Override
public boolean equals(Object obj) {
if(obj instanceof Book) {
Book book = (Book)obj;
if(this.bookNumber == book.bookNumber) {
return true;
}
else {
return false;
}
}
return false;
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return bookNumber;
}
}
public class ToStringEx {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Book book1 = new Book(200, "개미");
Book book2 = new Book(200, "개미");
System.out.println(book1);
System.out.println(book1.toString());
System.out.println(book1.equals(book2));
System.out.println(book1.hashCode());
System.out.println(book2.hashCode());
}
}
String 클래스와 Integer 클래스의 equals() 메서드는 재정의되어 있다고 했다. (이전 글에 관련 내용 있음)
그러면 hashCode() 메서드도 함께 재정의되어 있을 것이다.
public class HashCodeTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String str1 = new String("abc");
String str2 = new String("abc");
System.out.println(str1.hashCode());
System.out.println(str2.hashCode());
Integer i1 = new Integer(100);
Integer i2 = new Integer(100);
System.out.println(i1.hashCode());
System.out.println(i2.hashCode());
}
}
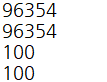
equals() 메서드의 결과 값이 true인 경우 hashCode() 메서드는 동일한 해시 코드 값을 반환한다.
Integer 클래스의 hashCode() 메서드는 정수 값을 반환하도록 재정의되어 있다.
'자바 기초' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 자바 String 클래스, StringBuffer, StringBuilder- Do it ! 자바프로그래밍기초 (0) | 2022.07.26 |
|---|---|
| 자바 clone() 메서드 - Do it ! 자바프로그래밍기초 (0) | 2022.07.25 |
| 자바 Object 클래스, toString, equals - Do it! 자바프로그래밍기초 (0) | 2022.07.25 |
| 자바 인터페이스 상속 - Do it! 자바프로그래밍 기초 (0) | 2022.07.22 |
| 자바 인터페이스 - Do it! 자바프로그래밍기초 (0) | 2022.07.22 |


